The dangers of radon gas and its protective measures
Radon is a colorless, odorless radioactive gas, mainly derived from the decay of uranium. It occurs widely in nature, especially in soil and rocks. Although radon gas is generally found in low concentrations in the air, in some areas, especially underground spaces, older homes, and airtight rooms, radon concentrations can increase significantly and pose a health risk.
Dangers of radon gas
Cancer risk: The biggest danger of radon is its effect on the respiratory system. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), radon is the second leading cause of lung cancer, after smoking. The decay products of radon can accumulate in the lungs, releasing radiation and damaging the DNA of lung cells, thereby increasing the risk of cancer.
Affects the immune system: Long-term exposure to high concentrations of radon may affect the body's immune system and reduce the body's ability to resist disease.
Potential environmental risks: Radon gas concentrations may be higher in some mining sites and in construction materials. This not only poses a threat to workers, but may also affect the health of surrounding people.
How to test for radon
Testing the concentration of radon gas is an important step in preventing its harm. There are a variety of radon testing devices on the market, and users can choose to conduct long-term or short-term testing at home. Long-term testing usually lasts more than 90 days, while short-term testing generally lasts between 2 and 7 days. Through detection, you can know the radon concentration in the living environment in time.
protective measures
To address the potential hazards of radon gas, the following protective measures can be taken:
Improve ventilation: Setting up a good ventilation system indoors and increasing air circulation can effectively reduce radon gas concentration. Especially in basements or enclosed rooms, maintaining air circulation is especially important.
Seal Cracks: Check your building’s walls, floors, and foundation for cracks and reduce the chance of radon gas seeping into your home by filling cracks and gaps.
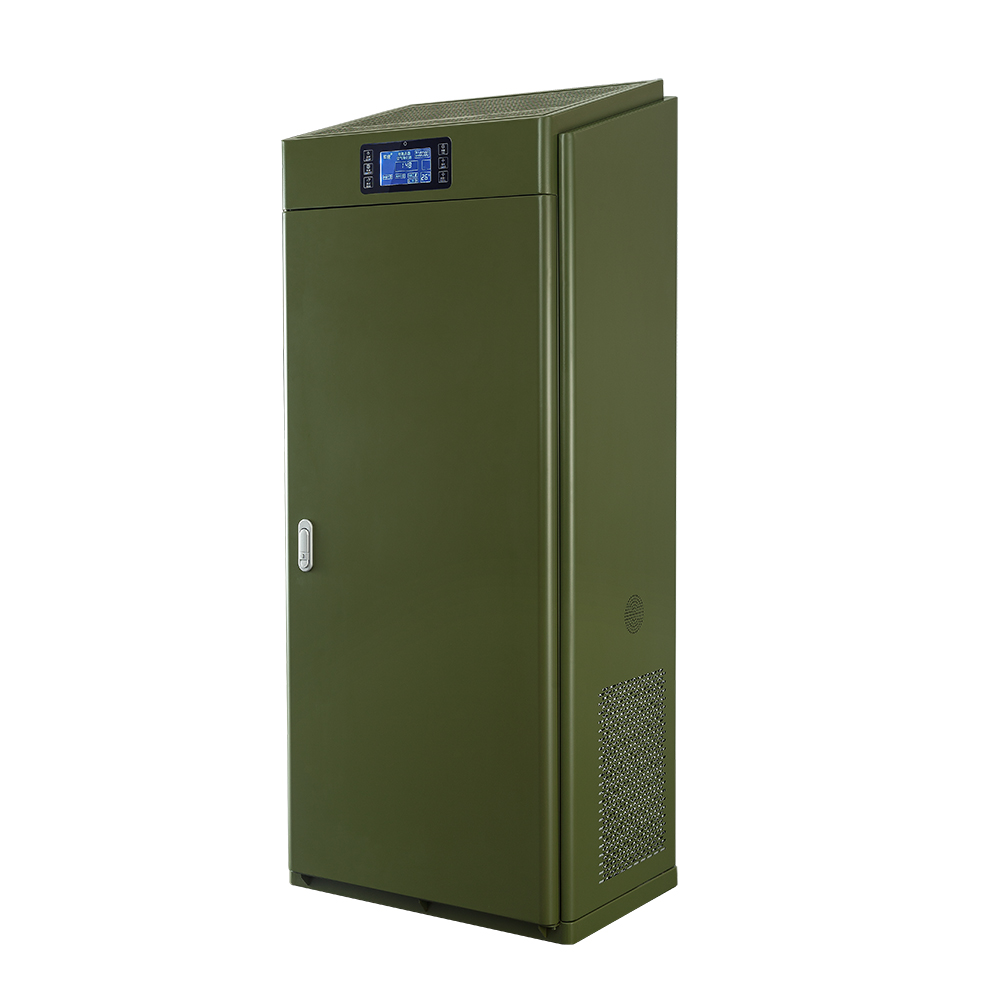
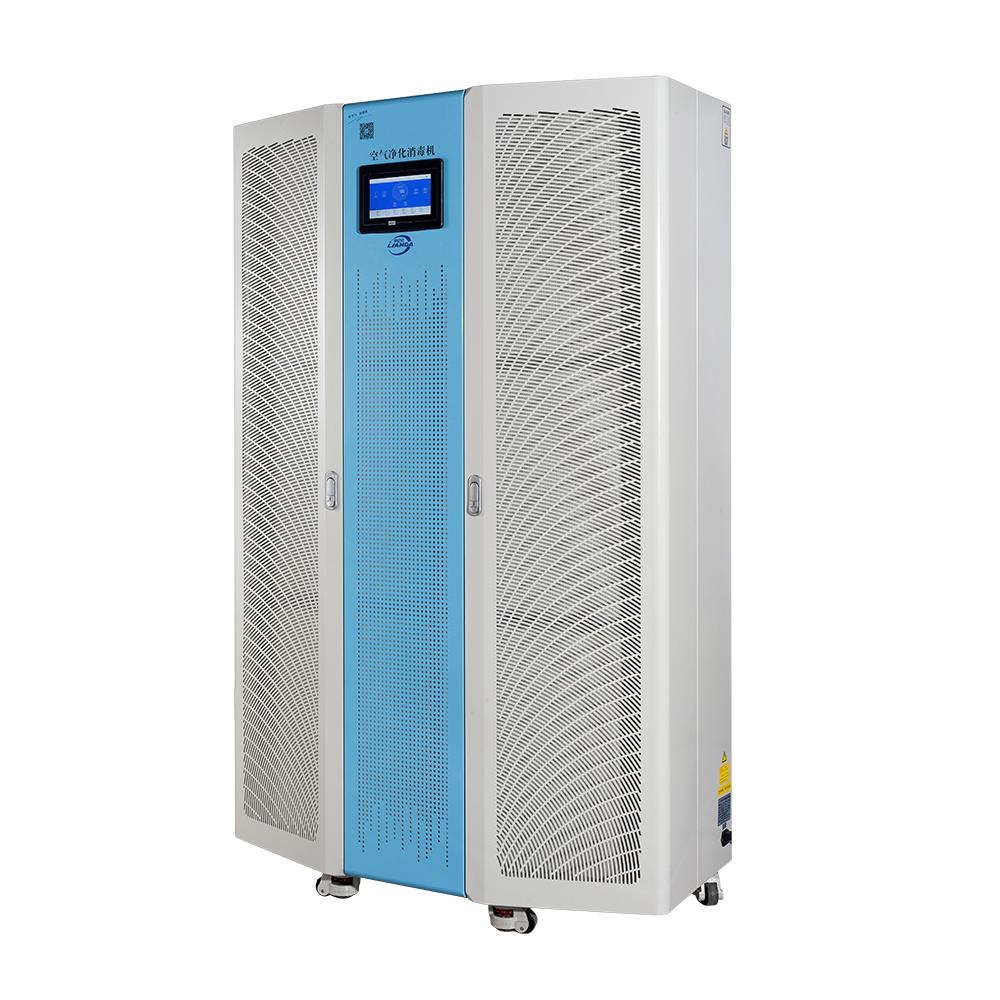
Install a radon mitigation system: For environments with high radon concentrations, consider installing a LAD radon-reducing air purifier to reduce radon concentrations.
Choose appropriate building materials: In newly built houses, choosing building materials with low radon gas emissions can reduce the production of radon gas to a certain extent.
Regular testing: Carry out regular radon testing to detect and solve potential radon problems in a timely manner to protect the health of family members.
As a naturally occurring radioactive gas, radon's hazards cannot be underestimated. Understanding the sources, hazards, and protective measures of radon gas is critical to protecting yourself and your family’s health. LAD radon reduction air purification equipment can not only monitor radon gas content, but also effectively reduce radon content. It is also mobile and very convenient, creating a safer living environment for us.